Hydrant System Overview as per AS 2419.1
Fire safety is an indispensable element in the design and maintenance of buildings and structures. Among the various components that contribute to fire safety, the fire hydrant system stands out as a fundamental provision for firefighting capabilities. In Australia, the standards for the design, installation, and commissioning of fire hydrant systems are encapsulated in the Australian Standard AS 2419.1. The most recent update, AS 2419.1:2021, has introduced pivotal modifications to enhance the efficacy of these systems in safeguarding properties against fire hazards.
Comprehensive Scope
The AS 2419 standard encompasses a broad spectrum of fire hydrant systems, which are utilized in diverse settings such as buildings, structures, storage yards, marinas, wharves, and industrial plants. It prescribes the minimum requirements for system performance, design, and installation, aiming to provide adequate fire protection across various environments.
Significant Revisions in AS 2419.1:2021
The 2021 revision of AS 2419.1 has been instrumental in updating the standard to reflect current fire safety needs:
- Exclusions: The standard now specifies that buildings exceeding an effective height of 135 meters, as well as warehouses classified under Class 7b and 8 with a total area surpassing 108,000 square meters, fall outside the purview of AS 2419.1:2021.
- Reticulation Main Residual Supply Pressure: The revised standard delineates methods to validate the main’s capacity to deliver unassisted flows and pressures under conditions that represent the 95th percentile.
- Booster System Requirements: The criteria for the necessity of a booster system have been updated. A booster is mandated when more than two feed hydrants are required to achieve coverage, which is a change from the previous stipulation of “more than six external hydrants.”
- Booster Placement: The preferred location for the installation of a booster has been revised to be within 20 meters of the main pedestrian entrance or at the main vehicle access point on the property boundary.
- Hydrant Flow Rates: For open deck car parks, categorized as Class 7a, the number of flowing outlets is now determined based on the size of the largest storey rather than the largest fire compartment.
Enhanced Coverage and Performance Standards
The performance of hydrant systems is paramount for effective firefighting operations. AS 2419.1:2021 categorizes fire hydrants and stipulates the requisite pressure and flow rates for different building types and areas. For example, in the absence of internal hydrants, external hydrants are capable of providing coverage for up to four levels above and one level below ground. Conversely, if internal hydrants are present, external hydrants can extend coverage to two levels above and one level below ground.
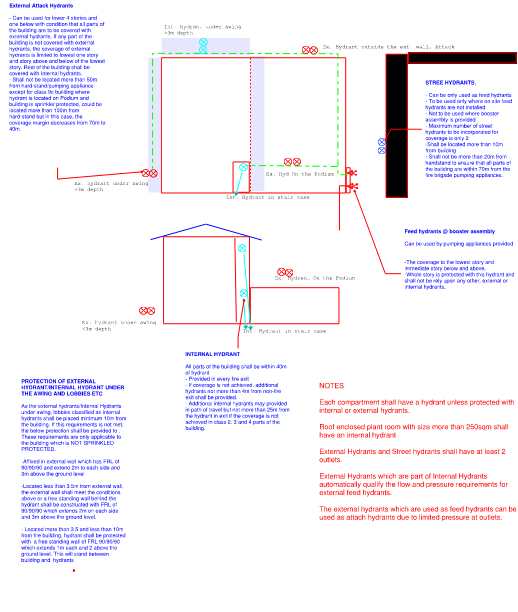
Types, Location and Protection of Hydrants
A Comprehensive of type, location and protection of hydrants is illustrated in attached picture for someone who is still developing the understanding of AS 2419.1. Someone can use the attached snapshot for reference as well. The illustration work of the picture represents that how in depth understanding of hydrants system has been developed by Cybil Consults.
In-Depth Conclusion
The amendments made to AS 2419.1:2021 are indicative of the evolving landscape of fire safety requirements and underscore the critical nature of maintaining a robust and efficient hydrant system. Compliance with these standards ensures that building owners and fire safety professionals equip their properties with the necessary tools to respond to fire emergencies effectively. This not only safeguards the occupants but also secures the assets within the property, offering a sense of security and protection. Cybil Consults provides consultancy in fire hydrant systems designing.