Introduction to Wet and dry Fire design Detection Systems
In a world where safety is paramount, Wet and dry Fire design detection systems play a crucial role in protecting lives and property. Whether it’s a residential building, a commercial establishment, or an industrial facility, the importance of early detection of fire cannot be overstated. One of the key decisions that building owners and managers face is choosing between Wet and Dry fire design detection systems, each governed by specific standards such as AS 2118, 2419, and 1670.
Understanding AS 2118, 2419, and 1670 Standards
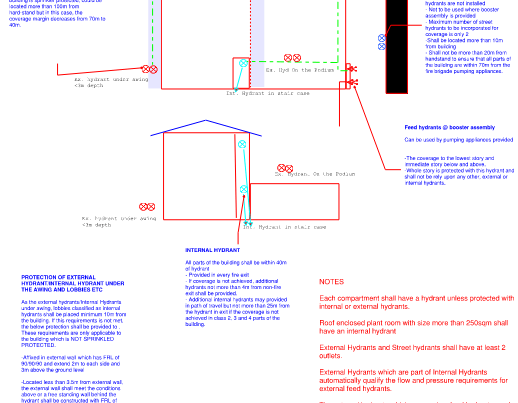
Before delving into the specifics of Wet and dry Fire design detection systems, it’s essential to understand the standards that regulate their design, installation, and maintenance. The AS 2118 standard provides guidelines for the design, installation, and commissioning of fire detection and alarm systems in buildings. Meanwhile, AS 2419 focuses on the design, installation, and commissioning of fire hydrant, hose reel, and hydrant booster systems. Lastly, AS 1670 governs the design, installation, commissioning, and maintenance of fire detection and alarm systems in buildings.
Wet Fire design Detection Systems
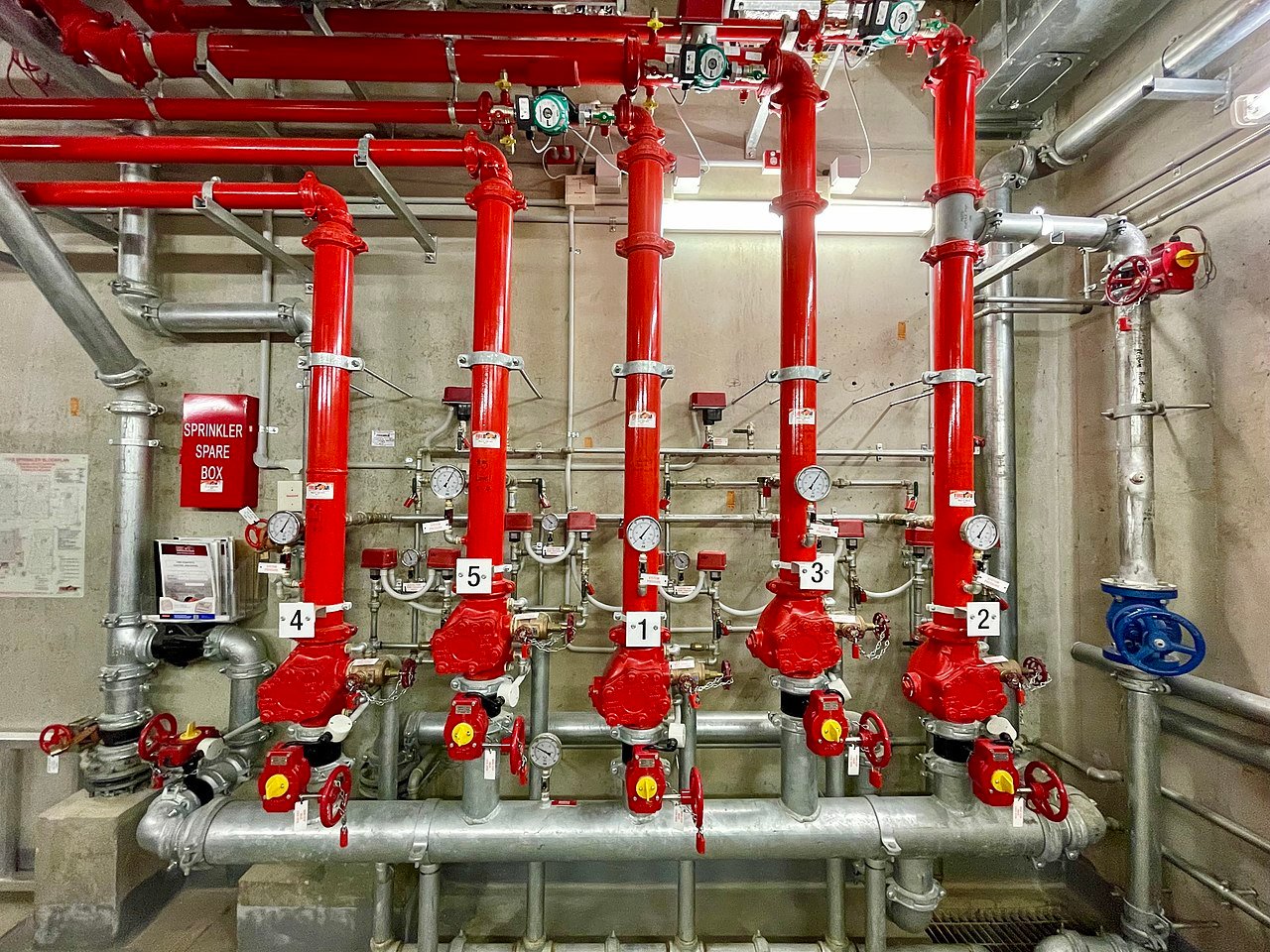
Wet fire detection systems utilize water as the primary extinguishing agent. These systems typically consist of a network of pipes connected to a water supply, with sprinkler heads strategically placed to cover the entire area. When a fire is detected, the sprinkler heads release water, suppressing the flames and preventing the spread of fire.
Dry Fire design Detection Systems
Unlike wet systems, dry fire detection systems use gases or chemicals as extinguishing agents instead of water. These systems are ideal for environments where water damage is a concern, such as data centers, museums, and libraries. Dry systems are activated by heat or smoke detectors, which trigger the release of the extinguishing agent.
Comparison between Wet and dry Fire design Detection Systems
Both wet and dry fire detection systems have their advantages and disadvantages. Wet systems are relatively cost-effective and easy to maintain but may cause water damage to property. On the other hand, dry systems are suitable for environments where water damage is a concern but require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Applications and Use Cases
The choice betweenWet and dry Fire design detection systems depends on various factors, including the type of building, occupancy, and environmental conditions. Wet systems are commonly used in residential buildings and commercial establishments, while dry systems are preferred in facilities where water damage is a significant concern, such as data centers and museums.
Key Considerations before Implementing Fire Detection Systems
Before installing a fire detection system, it’s essential to consider factors such as budget constraints, building structure, and regulatory compliance. Building owners and managers should conduct a thorough risk assessment to determine the most suitable type of system for their needs.
Future Trends in Wet and dry Fire design Detection Systems
Advancements in technology are driving innovation in the field of fire detection systems. From advanced sensors and detectors to integrated smart building systems, the future of fire safety looks promising. These advancements not only enhance the reliability and efficiency of fire detection systems but also improve overall building safety.
Case Studies
Real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of Wet and dry Fire design detection systems in preventing property damage and saving lives. Case studies highlight the benefits of early detection and rapid response, underscoring the importance of investing in robust fire detection systems.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Despite their proven effectiveness, Wet and dry Fire design detection systems are often subject to myths and misconceptions. Addressing these misconceptions is essential to ensure that building owners and managers make informed decisions about their safety measures.
Importance of Regular Maintenance and Testing
Regular maintenance and testing are crucial to ensure that fire detection systems perform optimally when needed. Building owners should schedule routine inspections and tests to identify and address any issues promptly.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
While the initial cost of installing a fire detection system may seem daunting, the long-term benefits far outweigh the investment. A cost-benefit analysis can help building owners assess the return on investment and make informed decisions about their safety measures.
Training and Education
Proper training and education are essential for the effective operation and maintenance of fire detection systems. Building owners should invest in training programs for maintenance personnel and ensure that users are familiar with emergency procedures.
Environmental Impact
In an increasingly eco-conscious world, sustainability considerations are becoming integral to fire detection system design. Eco-friendly alternatives and practices can minimize the environmental impact of fire detection systems while maintaining their effectiveness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Wet and dry Fire design detection systems play a crucial role in safeguarding lives and property against the devastating effects of fire. By understanding the differences between these systems and adhering to relevant standards and regulations, building owners can revolutionize their safety measures and provide peace of mind to occupants.